Setting Up VNC Session: Difference between revisions
m (→One Time Setup) |
Jpr@uab.edu (talk | contribs) (Refine documentation to improve flow and structure and fill in context) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Virtual Network Computing (VNC) is a cross-platform desktop sharing system to interact with remote system's desktop using a graphical | [[wikipedia:Virtual_Network_Computing|Virtual Network Computing (VNC)]] is a cross-platform desktop sharing system to interact with a remote system's desktop using a graphical interface. This page covers basic instructions to access a desktop on [[Cheaha]] using VNC. These basic instructions support a variety of use-cases where access to graphical applications on the cluster is helpful or required. If you are interested in knowing more options or detailed technical information, then please take a look at man pages of specified commands. | ||
== One Time Setup == | == One Time Setup == | ||
VNC use on Cheaha requires a one-time-setup to configure settings to starting the virtual desktop. These instructions will configure the VNC server to use the Gnome desktop environment, the default desktop environment on the cluster. (Alternatively, you can run the vncserver command without this configure and and start a very basic (but harder to use) desktop environment.) | |||
=== VNC Session Password === | |||
You must maintain a password for your VNC server sessions using the vncpasswd command. The password is validated each time a connection comes in, so it can be changed on the fly using vncpasswd command anytime later. Remember this password as you will be prompted for it when you try accessing the VNC session later. By default, the command stores an obfuscated version of the password in the file $HOME/.vnc/passwd. | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
$ vncpasswd | $ vncpasswd | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
=== VNC Desktop Selection === | |||
The vncserver command relies on a configuration script to start your virtual desktop environment. The [[wikipedia:GNOME|GNOME]] desktop provides a familiar desktop experience and can be selected by creating the following vncserver startup script (~/.vnc/xstartup). | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 16: | Line 18: | ||
#!/bin/sh | #!/bin/sh | ||
# | # Start up the standard system desktop | ||
unset SESSION_MANAGER | unset SESSION_MANAGER | ||
exec /etc/X11/xinit/xinitrc | exec /etc/X11/xinit/xinitrc | ||
| Line 25: | Line 27: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
This completes one-time setup | By default a VNC server displays graphical environment using a tab-window-manager. If the above xstartup file is absent, then a file with the default tab-window-manager settings will be created by the vncserver command during startup. If you want to switch to the GNOME desktop, simply replace this default file with the settings above. | ||
This completes the one-time setup for setting a VNC server password and selecting the preferred desktop environment. | |||
== Starting your VNC Desktop == | |||
Your VNC desktop must be started before you can connect to it. To start the VNC desktop you need to log into cheaha using an [[Cheaha_GettingStarted#Login|standard SSH connection]]. The VNC server is started by executing the vncserver command after you log in to cheaha. It will run in the background and continue running even after you log out of the SSH session that was used to run the vncserver command. | |||
To start the VNC desktop run the vncserver command. You will see a short message like the following from the vncserver before it goes into the background. You will need this information to connect to your desktop. | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
$ vncserver | $ vncserver | ||
| Line 36: | Line 42: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
The above command output indicates that a VNC server is started on VNC | The above command output indicates that a VNC server is started on VNC X-display number 24, which translates to system port 5924. The vncserver automatically selects this port from a list of available ports. | ||
The actual system port on which VNC server is listening for connections is obtained by adding a VNC base port (default: port 5900) and a VNC X-display number (24 in above case). Alternatively you can specify a high numbered system port directly (e.g. 5927) using '-rfbport <port-number>' option and the vncserver will try to use it if it's available. See vncserver's man page for details. | |||
Please note that the vncserver will continue to run in the backgound on the head node until it is explicitly stopped. This allows you to reconnect to the same desktop session without having to first start the vncserver, leaving all your desktop applications active. When you no longer need your desktop, simply log out of your desktop using the desktop's log out menu option or by explicitly ending the vncserver command with the 'vncserver -kill ' command. | |||
== Connecting to the VNC Server == | |||
As indicated in the output from the vncserver command, the VNC desktop is listening for connections on a higher numbered port. This port isn't directly accessible from the internet. Hence, we need to use SSH local port forwarding to connect to this server. | |||
This SSH session provides the connection to your VNC desktop and must remain active while you use the desktop. You can disconnect and reconnect to your desktop by establishing this SSH session whenever you need to access your desktop. In other words, your desktop remains active across your connections to it. This supports a mobile work environment. | |||
== | === Port-forwarding from Linux or Mac Systems === | ||
Set up SSH port forwarding using the native SSH command. | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
# ssh -L <local-port>:<remote-system-host>:<remote-system-port> USERID@<SSH-server-host> | # ssh -L <local-port>:<remote-system-host>:<remote-system-port> USERID@<SSH-server-host> | ||
$ ssh -L 5924:localhost:5924 USERID@cheaha.uabgrid.uab.edu | $ ssh -L 5924:localhost:5924 USERID@cheaha.uabgrid.uab.edu | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Above command will forward connections on local port 5924 to a remote system's (same as SSH server host Cheaha - hence localhost) port 5924. | Above command will forward connections on local port 5924 to a remote system's (same as SSH server host Cheaha - hence localhost) port 5924. | ||
=== Port-forwarding from Windows Systems === | |||
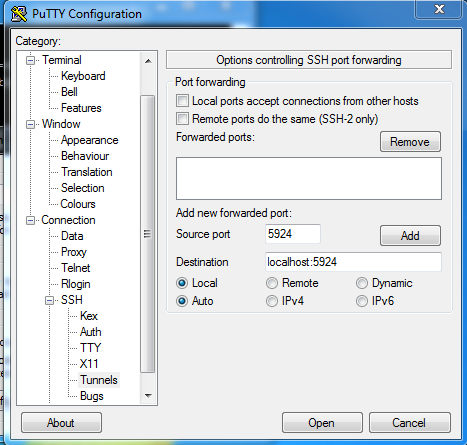
Windows users need to establish the connection using whatever SSH software they commonly use. The following is an example configuration using Putty client on Windows. | |||
[[File:Putty-SSH-Tunnel.png]] | [[File:Putty-SSH-Tunnel.png]] | ||
== Viewing your VNC Desktop == | |||
Once we have a local (client-side) port available for connecting to the VNC server, we can access the VNC desktop using a VNC client. | |||
=== Select a VNC Client === | |||
Mac OS comes with a native VNC client so you don't need to use any third-party software. Most Linux systems have the VNC software installed so you can simply use the vncviewer command to access a VNC server. | |||
If you use MS Windows then you will need to install a VNC client. Here is a list of VNC client softwares and you can any one of it to access VNC server. | |||
* http://www.tightvnc.com/ (Mac, Linux and Windows) | * http://www.tightvnc.com/ (Mac, Linux and Windows) | ||
* http://www.realvnc.com/ (Mac, Linux and Windows) | * http://www.realvnc.com/ (Mac, Linux and Windows) | ||
* http://sourceforge.net/projects/cotvnc/ (Mac) | * http://sourceforge.net/projects/cotvnc/ (Mac) | ||
=== Access your Desktop === | |||
Once we have a VNC client installed, we can access VNC server using the following connection string. Since we are using SSH local port forwarding to access our VNC server, the VNC client will be told to connect to your local machine. | |||
Mac users can use the following connection string in Finder: | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
# vnc://<vnc-server>:<vnc-port> | # vnc://<vnc-server>:<vnc-port> | ||
vnc://localhost:5924 | vnc://localhost:5924 | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Once we have a VNC session established with Gnome desktop environment, we can use it to launch any graphical application on | Linux users can use the command | ||
<pre> | |||
vncviewer :24 | |||
</pre> | |||
Windows users should use whatever connection string is applicable to their client. | |||
== Using your Desktop == | |||
Once we have a VNC session established with Gnome desktop environment, we can use it to launch any graphical application on Cheaha or use it to open GUI (X11) supported SSH session with a remote system in the cluster. | |||
VNC can be particularly useful when we are trying to access and X Windows application from MS Windows, as native X11 setup on Windows is typically more involved than the VNC setup above. For example, it's much easier to start X11 based SSH session with the remote system on the cluster from above Gnome desktop environment than doing all X11 setup on Windows. | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
$ ssh -X $USER@172.x.x.x | $ ssh -X $USER@172.x.x.x | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Revision as of 18:47, 14 January 2013
Virtual Network Computing (VNC) is a cross-platform desktop sharing system to interact with a remote system's desktop using a graphical interface. This page covers basic instructions to access a desktop on Cheaha using VNC. These basic instructions support a variety of use-cases where access to graphical applications on the cluster is helpful or required. If you are interested in knowing more options or detailed technical information, then please take a look at man pages of specified commands.
One Time Setup
VNC use on Cheaha requires a one-time-setup to configure settings to starting the virtual desktop. These instructions will configure the VNC server to use the Gnome desktop environment, the default desktop environment on the cluster. (Alternatively, you can run the vncserver command without this configure and and start a very basic (but harder to use) desktop environment.)
VNC Session Password
You must maintain a password for your VNC server sessions using the vncpasswd command. The password is validated each time a connection comes in, so it can be changed on the fly using vncpasswd command anytime later. Remember this password as you will be prompted for it when you try accessing the VNC session later. By default, the command stores an obfuscated version of the password in the file $HOME/.vnc/passwd.
$ vncpasswd
VNC Desktop Selection
The vncserver command relies on a configuration script to start your virtual desktop environment. The GNOME desktop provides a familiar desktop experience and can be selected by creating the following vncserver startup script (~/.vnc/xstartup).
$ cat > $HOME/.vnc/xstartup <<\EOF #!/bin/sh # Start up the standard system desktop unset SESSION_MANAGER exec /etc/X11/xinit/xinitrc EOF $ chmod +x $HOME/.vnc/xstartup
By default a VNC server displays graphical environment using a tab-window-manager. If the above xstartup file is absent, then a file with the default tab-window-manager settings will be created by the vncserver command during startup. If you want to switch to the GNOME desktop, simply replace this default file with the settings above.
This completes the one-time setup for setting a VNC server password and selecting the preferred desktop environment.
Starting your VNC Desktop
Your VNC desktop must be started before you can connect to it. To start the VNC desktop you need to log into cheaha using an standard SSH connection. The VNC server is started by executing the vncserver command after you log in to cheaha. It will run in the background and continue running even after you log out of the SSH session that was used to run the vncserver command.
To start the VNC desktop run the vncserver command. You will see a short message like the following from the vncserver before it goes into the background. You will need this information to connect to your desktop.
$ vncserver New 'cheaha.uabgrid.uab.edu:24 (pavgi)' desktop is cheaha.uabgrid.uab.edu:24 Starting applications specified in /home/pavgi/.vnc/xstartup Log file is /home/pavgi/.vnc/cheaha.uabgrid.uab.edu:24.log
The above command output indicates that a VNC server is started on VNC X-display number 24, which translates to system port 5924. The vncserver automatically selects this port from a list of available ports.
The actual system port on which VNC server is listening for connections is obtained by adding a VNC base port (default: port 5900) and a VNC X-display number (24 in above case). Alternatively you can specify a high numbered system port directly (e.g. 5927) using '-rfbport <port-number>' option and the vncserver will try to use it if it's available. See vncserver's man page for details.
Please note that the vncserver will continue to run in the backgound on the head node until it is explicitly stopped. This allows you to reconnect to the same desktop session without having to first start the vncserver, leaving all your desktop applications active. When you no longer need your desktop, simply log out of your desktop using the desktop's log out menu option or by explicitly ending the vncserver command with the 'vncserver -kill ' command.
Connecting to the VNC Server
As indicated in the output from the vncserver command, the VNC desktop is listening for connections on a higher numbered port. This port isn't directly accessible from the internet. Hence, we need to use SSH local port forwarding to connect to this server.
This SSH session provides the connection to your VNC desktop and must remain active while you use the desktop. You can disconnect and reconnect to your desktop by establishing this SSH session whenever you need to access your desktop. In other words, your desktop remains active across your connections to it. This supports a mobile work environment.
Port-forwarding from Linux or Mac Systems
Set up SSH port forwarding using the native SSH command.
# ssh -L <local-port>:<remote-system-host>:<remote-system-port> USERID@<SSH-server-host> $ ssh -L 5924:localhost:5924 USERID@cheaha.uabgrid.uab.edu
Above command will forward connections on local port 5924 to a remote system's (same as SSH server host Cheaha - hence localhost) port 5924.
Port-forwarding from Windows Systems
Windows users need to establish the connection using whatever SSH software they commonly use. The following is an example configuration using Putty client on Windows.
Viewing your VNC Desktop
Once we have a local (client-side) port available for connecting to the VNC server, we can access the VNC desktop using a VNC client.
Select a VNC Client
Mac OS comes with a native VNC client so you don't need to use any third-party software. Most Linux systems have the VNC software installed so you can simply use the vncviewer command to access a VNC server.
If you use MS Windows then you will need to install a VNC client. Here is a list of VNC client softwares and you can any one of it to access VNC server.
* http://www.tightvnc.com/ (Mac, Linux and Windows) * http://www.realvnc.com/ (Mac, Linux and Windows) * http://sourceforge.net/projects/cotvnc/ (Mac)
Access your Desktop
Once we have a VNC client installed, we can access VNC server using the following connection string. Since we are using SSH local port forwarding to access our VNC server, the VNC client will be told to connect to your local machine.
Mac users can use the following connection string in Finder:
# vnc://<vnc-server>:<vnc-port> vnc://localhost:5924
Linux users can use the command
vncviewer :24
Windows users should use whatever connection string is applicable to their client.
Using your Desktop
Once we have a VNC session established with Gnome desktop environment, we can use it to launch any graphical application on Cheaha or use it to open GUI (X11) supported SSH session with a remote system in the cluster.
VNC can be particularly useful when we are trying to access and X Windows application from MS Windows, as native X11 setup on Windows is typically more involved than the VNC setup above. For example, it's much easier to start X11 based SSH session with the remote system on the cluster from above Gnome desktop environment than doing all X11 setup on Windows.
$ ssh -X $USER@172.x.x.x