Cheaha: Difference between revisions
Jpr@uab.edu (talk | contribs) m (→Continuous Resource Improvement: Improved wording.) |
Jpr@uab.edu (talk | contribs) (→2008 Hardware Upgrade: Condense paragraph, fix typo) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
In 2008, money was allocated for hardware upgrades which lead to the acquisition of an additional 192 cores based on the Intel Quad-Core E5450 3.0Ghz CPU in August of 2008. This hardware represented a major technology upgrade that included space for additional expansion to address over-all capacity demand and enable resource reservation. | In 2008, money was allocated for hardware upgrades which lead to the acquisition of an additional 192 cores based on the Intel Quad-Core E5450 3.0Ghz CPU in August of 2008. This hardware represented a major technology upgrade that included space for additional expansion to address over-all capacity demand and enable resource reservation. | ||
This upgrade also included enhancements to enable access to the aggregate compute power available to the UAB community and improve management of compute jobs across clusters that are part of the UABgrid computing infrastructure. | This upgrade also included enhancements to enable access to the aggregate compute power available to the UAB community and improve management of compute jobs across clusters that are part of the UABgrid computing infrastructure. 10Gigabit Ethernet connectivity to the UABgrid Research Network supports high speed data transfers between clusters connected to this network, enabling efficient job staging on multiple resources. [http://www.gridway.org GridWay-based] meta-scheduling enables management of compute jobs across cluster boundaries and brings grid-computing into production. | ||
10Gigabit Ethernet connectivity to the UABgrid Research Network supports high speed data transfers between clusters connected to this network, enabling efficient job staging on multiple resources. [http://www.gridway.org GridWay-based] meta-scheduling | |||
=== Continuous Resource Improvement === | === Continuous Resource Improvement === | ||
Revision as of 20:19, 13 January 2009
Cheaha is a shared high-performance computing (HPC) resource sponsored by UAB Information Technology (UAB IT). Cheaha is available to members of the UAB community to support research activities in need of enhanced computational capacity.
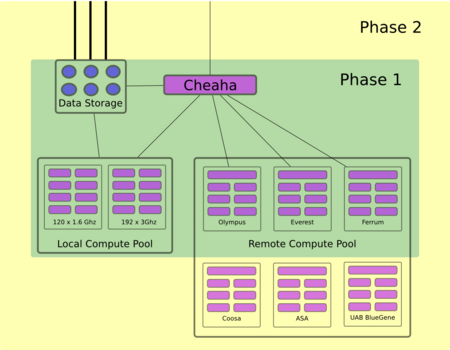
Cheaha includes a dedicated pool of local compute resources and can provide seamless access to remote compute resources through the use of grid computing technologies. The local compute pool contains two resource banks based on the x86_64 64-bit architecture. 192 3.0Ghz cores and 120 1.6Ghz cores combine to provide nearly 3TFlops of dedicated computing power.
Use of the local compute pool is controlled via scheduling policies designed to maximize availability of total capacity and ensure guaranteed access to reserved resources. Use of the remote compute pool is contingent upon allocations for individual users on specific remote resources. Incorporation of remote resources enables simplified account management for HPC users and can significantly increase the total compute capacity available for HPC jobs.
Cheaha is located in the UAB Shared Computing facility in BEC. Resource design and development is lead by UAB IT Infrastructure Services in open collaboration with community members. Development effort is coordinated though a dedicated project web site. Operational support is provided by the UAB School of Engineering's cluster support group.
Cheaha is named in honor of Cheaha Mountain, the highest peak in the state of Alabama. Cheaha's summit offers panoramic vistas of the surrounding landscape (Cheaha photo-stream on Flikr).
History
In 2002 UAB was awarded an infrastructure development grant through the NSF EPsCoR program. This led to the 2005 acquisition of a 64 node compute cluster with 2 AMD Opteron 242 1.6Ghz CPUs per node (128 total cores). This cluster was named Cheaha. Cheaha expanded the compute capacity available at UAB and was the first general-access resource for the community. It lead to expanded roles for UAB IT in research computing support through the development of the UAB Shared HPC Facility in BEC and provided further engagement in Globus-based grid computing resource development on campus via UABgrid and regionally via SURAgrid.
2008 Hardware Upgrade
In 2008, money was allocated for hardware upgrades which lead to the acquisition of an additional 192 cores based on the Intel Quad-Core E5450 3.0Ghz CPU in August of 2008. This hardware represented a major technology upgrade that included space for additional expansion to address over-all capacity demand and enable resource reservation.
This upgrade also included enhancements to enable access to the aggregate compute power available to the UAB community and improve management of compute jobs across clusters that are part of the UABgrid computing infrastructure. 10Gigabit Ethernet connectivity to the UABgrid Research Network supports high speed data transfers between clusters connected to this network, enabling efficient job staging on multiple resources. GridWay-based meta-scheduling enables management of compute jobs across cluster boundaries and brings grid-computing into production.
Continuous Resource Improvement
The 2008 upgrade began a phased development approach for Cheaha with on-going increases in capacity and feature enhancements being brought into production via an open community process. The first two phases are represented in the diagram on the right, which highlights the logical connectivity between resources. Phase 1 is scheduled for production in January 2009.